Are you ready to level up your web development skills? Hosting a Web API with HTTPS in IIS can be a game-changer for your projects, ensuring security and reliability.
Imagine transforming your applications into robust, secure platforms that users trust. This guide will walk you through the process, step by step, so you can confidently deploy your API and protect your data. You’ll discover tips and tricks to simplify the setup and make your API shine in the digital landscape.
Dive in now to unlock the potential of your web applications and elevate your skills to new heights!
Setting Up Iis
Open the Control Panel on your computer. Select Programs, then click on Turn Windows features on or off. A new window will appear. Find and check the box for Internet Information Services (IIS). Click OK and wait for the installation to complete. You might need to restart your computer. This process makes your computer ready to host web applications.
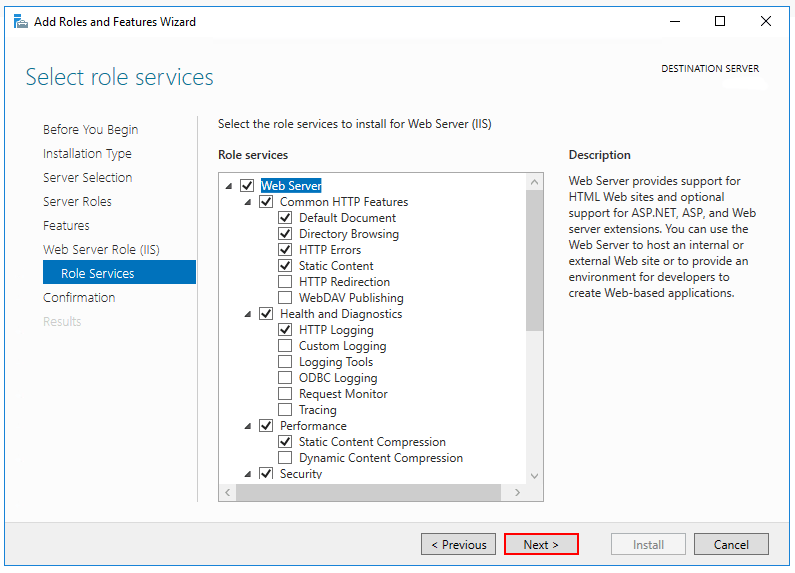
Open the IIS Manager from the start menu. Click on Sites in the left panel. Right-click and select Add Website. Enter a name for your website. Set the physical path to your Web API folder. Under Binding, choose HTTPS. Add your SSL certificate. This step ensures secure connections. Click OK to save. Your Web API is now configured with HTTPS.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Preparing Web Api For Deployment
Start by creating a new Web API project in your development tool. Choose a template that fits your needs. Add the necessary controllers and models. These will define how your API works. Test your API locally to ensure it functions well. Fix any errors you find. This makes sure the API is ready for users. Keep your code simple and clear. This helps when updating or fixing it later.
HTTPS keeps data safe and secure. First, obtain a valid SSL certificate. This certificate proves your site is secure. Configure your API to use HTTPS by default. Check your API settings. Make sure they point to the correct certificate. Test your API again. Ensure it works with HTTPS. Users should see a lock icon in their browser. This tells them the connection is secure.
Deploying Web Api To Iis
First, open your Web API project. Click on the Build menu at the top. Select Publish from the dropdown. Choose a folder as the publish target. Click Next. Now, give a path where you want to publish. Click Finish to start publishing. Wait until the process completes. Your files are now ready.
Go to Control Panel. Click on Administrative Tools. Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. Right-click on Sites. Choose Add Website. Give a name to your site. Browse to the path of your published files. Set the binding to HTTPS. Click OK to create the application. Now, your Web API is hosted on IIS with HTTPS.

Credit: learn.microsoft.com
Configuring Https In Iis
First, get an SSL certificate from a trusted provider. This ensures your site is secure. Install the certificate on your server. Use the IIS Manager to do this. Find the “Server Certificates” option. Click on it. Then, follow the steps to add your SSL certificate. Your site will now be ready for HTTPS.
Next, bind HTTPS to your Web API. Open IIS Manager again. Find your site in the list. Click on it. Select “Bindings” from the menu on the right. Add a new binding. Choose “https” from the type list. Select your SSL certificate. Save the changes. Your Web API is now running with HTTPS. This keeps data safe during transfer.
Testing The Hosted Web Api
Hosting a Web API in IIS with HTTPS ensures secure data transmission. Start by installing an SSL certificate on your server. Configure IIS to bind the Web API to HTTPS, enhancing security and reliability.
Accessing Web Api Via Https
Accessing your Web API through HTTPS ensures secure communication. Open a browser. Enter the URL of your Web API. Start with https://. Check if the connection is secure. Look for a padlock symbol. This confirms secure access. No padlock? Check your SSL certificate. Ensure it’s properly installed. Proper installation is crucial for security.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Sometimes, Web API might not work. Check your firewall settings. It might block HTTPS requests. Ensure it’s configured correctly. Incorrect settings can cause issues. Check the binding in IIS. It should include HTTPS. Verify your SSL certificate. An expired certificate causes problems. Ensure it’s up to date. Check the URL entered. A typo can lead to errors. Correct these to fix access issues.
Security Considerations
SSL certificates are like a safety badge for your website. They keep data safe and private. You need to install them correctly. This helps avoid errors and keeps users safe. Always renew your SSL certificates on time. Expired certificates can scare users away. They make your site look unsafe. Use a trusted certificate authority to get your SSL certificate. This builds trust with users.
Authentication checks if users are who they say. It is like a lock on a door. Use strong passwords for added security. Multi-factor authentication is even better. It adds another layer of protection. Users might need to enter a code sent to their phone. This keeps bad people out. Always use up-to-date authentication methods. Technology changes fast. Stay current to stay safe.
Performance Optimization
Caching helps speed up API responses. It stores data temporarily. This reduces server load. Set cache headers in your API. Choose how long data stays cached. Use tools to manage cache. Monitor cached data regularly. This ensures it’s up-to-date. Avoid caching sensitive information. Secure it properly. Proper caching improves user experience.
Monitoring helps track API performance. Check response times often. Look for slow endpoints. Analyze server logs. This finds errors quickly. Use monitoring tools. They send alerts for issues. Monitor traffic patterns. Identify peak times. This helps plan server capacity. Improve API performance with regular checks.
Credit: learn.microsoft.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How To Enable Https In Iis For Web Api?
To enable HTTPS in IIS, first obtain an SSL certificate. Then, open IIS Manager, select your site, and click on “Bindings. ” Add a new binding with type “https” and assign the certificate. Ensure that your Web API configuration allows HTTPS traffic.
Why Use Iis For Hosting Web Api?
IIS offers robust features for hosting Web APIs, including security, scalability, and easy management. It supports HTTPS, which is essential for secure communication. IIS integrates well with Windows environments, providing reliable performance and extensive logging capabilities to monitor your API.
Can I Host Web Api Without Https?
Yes, you can host a Web API without HTTPS, but it’s not recommended. HTTP lacks encryption, making data susceptible to interception. HTTPS encrypts data in transit, ensuring confidentiality and integrity. For security and compliance, always use HTTPS for Web APIs.
How To Troubleshoot Https Issues In Iis?
Start by checking your SSL certificate validity and bindings in IIS Manager. Ensure the certificate matches the domain. Verify that the server’s firewall allows HTTPS traffic. Review IIS logs for error details and consider using tools like SSL Labs for further diagnosis.
Conclusion
Securing your Web API with HTTPS in IIS is essential. It protects data and builds trust. Follow steps carefully for smooth setup. Always test your API after configuration. Check for any errors. Ensure your SSL certificate is valid and up to date.
This boosts security and performance. HTTPS ensures data integrity. It prevents unauthorized access. Your users will appreciate the added security. A secure API enhances user experience. It also complies with security standards. Maintain regular updates and monitoring. Stay proactive to keep your API secure.
This will safeguard your application and user information effectively.



