Imagine the thrill of seeing your very own web application live on the internet, accessible to users around the globe. Whether you’re a budding developer or simply curious about the process, building and hosting a web application can be an exciting venture.
You might think it’s complex and daunting, but with the right guidance, you can master it efficiently. This article will walk you through the essential steps, simplifying the technical jargon into clear actions. You’ll learn how to design, develop, and host your application, making it accessible to anyone with an internet connection.
Picture yourself transforming ideas into interactive experiences, and feel the satisfaction of your work being appreciated by users everywhere. Stick around, and you’ll discover practical tips and tricks that can make this journey smoother and more enjoyable. Unlock the potential of your creativity and technical skills, and see how you can make your web application stand out in the digital landscape. Ready to dive in? Let’s get started!
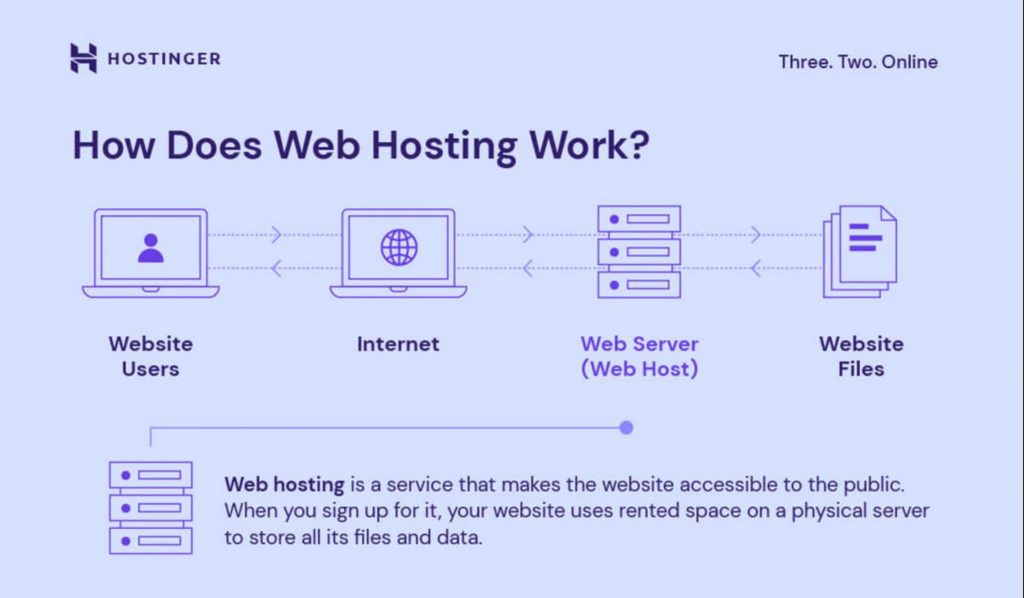
Credit: www.hostinger.com
Choosing The Right Framework
Many frameworks exist for building web apps. Some are very popular. React is a top choice. It is made by Facebook. Angular is another one. Google made it. Vue.js is a third popular framework. It is easy to learn. Each has unique features. Some are fast. Others are easy. Many developers love these frameworks. Choosing depends on needs.
Ease of use is important. A framework should be simple. Community support helps a lot. More support means more help. Documentation should be clear. This helps learn quickly. Performance matters for speed. Fast apps are better. Scalability is key. Apps should grow with users. Security is also important. Protect user data always. Consider these factors carefully. They help in choosing the best framework.
Designing The Application Architecture
The frontend is what users see and interact with. It includes buttons, text, and images. The backend is the hidden part. It processes data and stores information. Think of the frontend as a shop window. The backend is the storeroom. Both parts need to work together smoothly. Good communication between them is key. This makes the application run well.
In a monolithic structure, everything is in one piece. All parts are connected closely. This can be simple to build. But, changes can be hard. In microservices, each part is separate. They work independently. It is like having many small apps. Each does a specific job. Updating or fixing one is easier. This makes it flexible and efficient.
Setting Up The Development Environment
Building a web app needs some basic tools. First, install a code editor. A code editor helps you write code. Some popular editors are Visual Studio Code and Sublime Text.
Next, a package manager is useful. It helps install libraries. Examples are npm for JavaScript and pip for Python. These make coding easier and faster.
A version control system keeps your code safe. It tracks changes and helps collaborate with others. Git is a popular choice. It lets you save code versions.
Use GitHub or GitLab to store code online. They are like a backup for your code. Easy to share and work together.
Credit: v0.dev
Developing The Web Application
Using clean and simple code is important. It helps others read your work. Always use meaningful names for variables and functions. This makes the code easier to understand. Keep your code organized and neat. Break long code into small parts. This helps in finding mistakes. Comments are also helpful. They explain what the code does. This is useful for you and others.
Testing finds errors in the code. Use tests to check each part of your app. There are tools to help with this. Debugging fixes the errors found. Look at error messages carefully. They give clues about what is wrong. Fix one error at a time. This is the best way to solve problems. Patience is important in debugging. It takes time to find and fix errors.
Database Integration
Selecting a database is important for a web app. Databases store all your information. Popular choices include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB. MySQL is great for simple apps. PostgreSQL handles complex data well. MongoDB is perfect for large, unstructured data. Consider your app’s needs before choosing. Think about data size. Think about speed. Think about security. Each database has its strengths. Choose wisely to ensure smooth performance.
Linking your app to a database is crucial. Connection allows your app to access stored data. Use database drivers to help connect. Drivers are like bridges. They help your app talk to the database. Make sure your app’s code is correct. Double-check settings. Ensure login credentials are secure. Always test the connection. If it works, your app can use the database easily.
Implementing Security Measures
Building and hosting a web application requires strong security measures. Protect data with firewalls, encryption, and regular updates. Secure coding practices help prevent vulnerabilities.
Data Protection
Keeping data safe is very important. Use encryption to protect data. Encryption changes data into secret code. Only the right key can unlock it. This keeps data safe from bad people. Use SSL certificates for websites. SSL keeps data private between the user and the site. Always update software. New updates fix security problems. Strong passwords help too. Use letters, numbers, and symbols. Make it hard to guess.
Authentication And Authorization
Authentication checks who you are. Use usernames and passwords for this. Sometimes, use extra steps like a code from a phone. This is called two-factor authentication. It makes accounts safer. Authorization decides what you can do. It gives permissions. Some people can see more things than others. This keeps important parts safe. Only trusted users should access sensitive data.
Optimizing Performance
Caching stores data for quick access. This reduces load times. It saves data from previous visits. Browsers use cache to load websites faster. Servers also cache data. This helps handle more users. Cached data stays safe on your device. It can be cleared anytime. Use strong caching rules. These improve speed and user experience.
Load balancing shares tasks among servers. This keeps apps fast. Servers work together to handle traffic. They prevent overload and crashes. More servers mean better performance. They make sure no server is too busy. Traffic spreads evenly across servers. This ensures smooth user experience. Monitoring servers helps spot issues early.
Deploying The Application
Deployment platforms help your app go live. Choose the right one. It can be cloud-based or server-based. Popular options include Heroku, AWS, and Azure. They offer easy setup. Each platform has unique features. Pick one that suits your needs. Consider scalability, cost, and support. This will make your app run smoothly.
With Continuous Integration and Deployment, updates are automatic. This process saves time. It ensures your app is always current. Tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, and GitLab are useful. They make deploying easy. Test before deploying to catch errors early. This keeps your app reliable. Regular updates improve user experience. Your app stays secure and efficient.
Hosting Options
Shared hosting is a basic option. Here, many websites use one server. This makes it cost-effective for beginners. But, it can be slow sometimes. If one site gets busy, others may slow down too. It’s simple to set up and good for small sites. Beginners find it easy to use. Control panels are provided, which are user-friendly. But, resources are limited. Not ideal for heavy traffic sites.
Dedicated hosting offers a private server. This means better performance and more control. Ideal for large websites with high traffic. It is more expensive than shared hosting. Users have full control over settings. This hosting provides more security. Suitable for websites needing many resources. Knowledge of server management is needed.
Cloud hosting uses many servers. This offers great scalability. Resources can be increased easily. It is suitable for growing businesses. If one server fails, others keep the site running. This makes it reliable. Costs depend on usage, which can be beneficial. It provides flexibility and speed. Technical knowledge is helpful but not always needed.
Domain And Ssl Configuration
Choose a unique domain name. Make sure it is easy to remember. Visit a domain registrar website. Examples include GoDaddy or Namecheap. Search for your chosen name. If it is available, purchase it. Add extra features like privacy protection. This keeps your information safe. Pay for the domain yearly or for multiple years.
SSL certificates protect your website. They keep data safe. Choose a trusted certificate provider. Examples are Let’s Encrypt or DigiCert. Install the certificate on your server. Follow the provider’s instructions. This process might require technical help. Check if the SSL is working. Look for a lock icon in the browser. It means your site is secure.
Monitoring And Maintenance
Building a web application requires ongoing monitoring and maintenance. Regular updates and security checks ensure smooth performance. Monitoring tools help detect issues early, keeping your application running efficiently.
Tracking Application Performance
It’s important to watch how your app runs. Check if it’s fast or slow. Look for errors that stop it from working. Use tools to see what is happening. Performance monitoring helps find problems early. It makes sure everything runs well. This keeps users happy.
Routine Updates
Apps need updates to stay safe and work well. Updating fixes bugs and adds new features. Make a list of updates needed. Do them regularly, like once a month. Regular updates keep your app strong and secure. They help it stay useful for everyone.
Credit: learn.microsoft.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Deploy My Web Application In The Internet?
Deploy your web application by choosing a hosting provider, uploading your files, and configuring server settings. Ensure your domain points to the server. Test the application to confirm functionality. Use a deployment tool like FTP, SSH, or cloud platforms for efficiency and manageability.
How Do I Host My Own Web Application?
Choose a web hosting provider, register a domain name, and set up a server environment. Deploy your web application files, configure necessary settings, and ensure security measures. Regularly update and maintain your application for optimal performance.
How Do I Host A Website On The Internet?
To host a website, choose a reliable hosting provider and register a domain. Upload your website files using FTP or the hosting control panel. Ensure the website is optimized for performance and security. Test the site to confirm it loads correctly and is accessible to users.
How Much Does It Cost To Build A Web App?
The cost to build a web app ranges from $5,000 to $250,000. Factors include features, design, and developer rates. Small projects cost less, while complex ones require more investment. Ensure clear requirements to get accurate estimates from developers.
Conclusion
Building and hosting a web application can be simple. Follow the steps carefully. Choose the right tools. Create a strong foundation. Set up your server. Test everything thoroughly. Make sure your application is secure. Keep your web app updated. This ensures smooth performance.
Building a web app is rewarding. It enhances your online presence. Brings your ideas to life. With patience, you’ll succeed. Happy coding and hosting!



