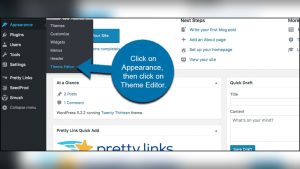
Are you ready to give your WordPress site a unique look that truly reflects your brand? Building a custom theme in WordPress might be the perfect solution for you.
Imagine having full control over your site’s design, layout, and functionality—tailored exactly to your needs. This article is your gateway to transforming your website into a standout masterpiece. We’ll guide you through the essential steps and tips to create a custom theme that not only captivates your audience but also enhances your site’s performance.
By the end, you’ll have the skills and confidence to craft a digital space that’s as unique as you are. Dive in and discover how you can turn your creative vision into reality with WordPress!
Getting Started
Creating a custom theme requires some basic tools. A text editor is essential. Options like Sublime Text or Notepad++ are popular. They help you write and edit code easily.
A web browser is also needed. Use it to test your theme. Chrome or Firefox are good choices. Don’t forget FTP software. It helps you upload files to your website. FileZilla is a free and easy option.
Finally, install WordPress on your local computer. This lets you test changes before going live. Tools like MAMP or XAMPP help with local installation.
Start by downloading WordPress from its official site. Follow the instructions to install it. You need a database for WordPress. Create it using phpMyAdmin. Make sure you remember the database name.
Next, open the wp-config.php file. Add your database details here. This connects WordPress to your database. Finally, open your browser and navigate to your local server. Follow the steps to complete the setup.

Credit: webdesignerwall.com
Theme Anatomy
Every WordPress theme needs some core files. These files help the theme work. The main file is style.css. It controls how your site looks.
The functions.php file is important too. It adds features to your theme. Other files like index.php and header.php are basic. They shape the theme’s structure.
Directories are like folders. They keep files organized. Common directories include images, scripts, and templates. Each has a special role in the theme.
Template hierarchy is like a map. It decides which file shows on your site. The index.php file is the fallback. Other templates are more specific. Like single.php for posts.
Template hierarchy checks files in order. It starts with the most specific. Then moves to more general ones. Knowing this helps you control your site’s look.
Creating A Basic Theme
Start by creating a new folder. This folder will hold your theme files. Name it something simple. Keep the name short and clear. Inside this folder, you’ll add important files. These files help WordPress understand your theme. Without them, your theme won’t work.
The style.css file is key. It tells WordPress about your theme. Add the theme name, author, and version inside. The index.php file is also important. It controls how your website looks. Both files must be in your theme folder. Without them, WordPress can’t use your theme.
Enqueueing Scripts And Styles
Using wp_enqueue_style is key for adding stylesheets. It helps keep your theme tidy. You must register each stylesheet. Use wp_enqueue_style function. It takes handle, source, dependencies, version, and media. Each stylesheet needs a unique handle. This makes it easy to manage. You can link stylesheets from external sources. Just provide the URL in the function. Don’t forget to call the function inside functions.php file.
Integrating JavaScript is similar to styles. Use wp_enqueue_script function. It helps add JavaScript files. You can set dependencies like jQuery. This ensures scripts load in order. Always register scripts before enqueueing. Use the same functions.php file. Keep your theme fast and organized. Ensure scripts load only when needed.
Designing The Header And Footer
The header.php file is crucial. It starts your theme. It contains code for the top part of your website. Open a text editor. Create a new file named header.php. Add HTML tags like and . Include WordPress functions like php wp_head(); ?. This function ensures all plugins work. Save the file.
The footer.php file finishes your theme. It contains code for the bottom part of your website. Create a new file named footer.php. Add HTML tags like and . Include the WordPress function php wp_footer(); ?. This function is important for scripts. Save the file. Your header and footer are ready!
Customizing Page Templates
Crafting custom page templates in WordPress allows for unique website designs. This approach provides flexibility in layout and style. Personalize your site to match your specific needs and brand identity.
Creating Custom Page Templates
WordPress themes allow creating custom page templates. These templates make each page look different. Start by copying an existing template file. Name it with a unique name, like custom-page.php. Open this file and add a special comment at the top. For example: php / Template Name: Custom Page / ?. This lets WordPress know about the new template. Assign this template to any page from the WordPress dashboard. It gives that page a unique layout and design.
Using Template Tags
Template tags are like special codes. They help display content dynamically. Use template tags in custom templates to show posts, titles, or dates. For example, php the_title(); ? shows the title of a post. php the_content(); ? shows the main content. These tags make templates more flexible. They adjust automatically to show the right content. Explore more tags to enhance your custom design.
Adding Dynamic Features
Integrating WordPress Loop is crucial for theme building. The WordPress Loop helps display posts dynamically. It pulls content from the database. You can show posts, pages, or custom posts. Use have_posts() and the_post() functions. These functions help fetch content easily. Place these functions in your theme’s files. They ensure dynamic content display. This makes your website more interactive. Remember, a dynamic site attracts visitors. It keeps them engaged longer.
Using Custom Post Types adds variety to your site. They allow different content types. Not just regular posts or pages. Use them for portfolios, testimonials, or products. Register custom post types with register_post_type(). This function is added in your theme’s functions.php file. It gives your site a unique touch. Custom post types make browsing more fun. They cater to different audience needs. It’s a great way to showcase varied content.

Credit: www.dreamhost.com
Styling With Css
Creating a custom theme in WordPress involves using CSS to design unique styles. Customize layout, colors, and fonts to match your vision. Enhance user experience by personalizing appearance and functionality, making your website stand out.
Responsive Design Techniques
CSS helps websites work well on all devices. Responsive design changes the look for different screens. Use percentages instead of fixed sizes. This helps the site fit any screen. Media queries are important. They change styles based on screen size. Flexbox and Grid are great tools. They make layouts easy to build. Images should be flexible too. Use max-width: 100% for images. This keeps them inside their containers.
Using Css Preprocessors
CSS preprocessors make writing styles easier. Sass and LESS are popular choices. They let you use variables. Variables save time and keep styles consistent. Nesting is another feature. It helps organize styles better. Mixins are handy too. They allow you to reuse styles. Preprocessors also have functions. Functions do math and change colors. All these features help build themes faster. They make CSS smarter and cleaner.
Enhancing With Javascript
Craft custom WordPress themes with JavaScript. Enhance functionality and style with dynamic features. Create unique user experiences effortlessly.
Adding Interactivity
JavaScript makes your website interactive. It can change elements on your page. Buttons can change color. Images can move. Forms can show messages. This makes your site fun and engaging. Users spend more time on interactive sites.
Utilizing Javascript Libraries
Libraries like jQuery and React make coding easier. They have ready-made code blocks. You can use them to create features quickly. They help in building things like sliders and pop-up windows. Libraries save time and reduce coding errors.
Testing And Debugging
Debugging is important in WordPress theme building. It helps find mistakes. There are useful tools for this. Debug Bar is a popular choice. It shows errors and warnings. Another tool is Query Monitor. It checks database queries. These tools help in fixing problems.
Tools For Debugging
- Debug Bar: Shows errors and warnings.
- Query Monitor: Checks database queries.
- Theme Check: Tests theme against WordPress standards.
Common Issues And Fixes
Themes often have issues. Sometimes they load slow. This may be due to large images. Resize images to speed up. Another problem is broken links. Check links regularly. Update them if broken. Themes may also have styling errors. Use CSS tools to fix these.
Making The Theme Mobile-friendly
Responsive design makes your site look good on all screens. It’s important to use flexible grids and layouts. This helps in fitting content on various screen sizes. CSS media queries are essential. They help in adjusting styles based on the device. Images should be scalable and not fixed in size. Use percentages instead of pixels. This ensures images resize properly. Test your website often to see how it looks. A well-designed site makes users happy.
Testing on different devices is crucial. Check your theme on phones, tablets, and computers. Each device may show your site differently. Simulators can help but real devices are better. Ask friends to test on their devices too. Fix any issues they find. Your goal is a smooth user experience. Keep your design consistent across all platforms. Happy users stay longer on your site.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Preparing For Deployment
Crafting a custom theme in WordPress involves creating unique designs and functionalities tailored to specific needs. Start by setting up a local development environment and familiarize yourself with WordPress theme structure. Utilize PHP, HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to build templates and styles, ensuring compatibility with WordPress standards.
Optimizing Performance
Fast websites keep visitors happy. Compress images to reduce load time. Use caching plugins to store site data. Minimize CSS and JavaScript files. Limit the number of plugins in use. Choose lightweight themes for better speed. Monitor site performance using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights. Make sure the server has enough resources. Regularly update your theme and plugins.
Final Checks Before Launch
Test your website on different devices. Verify all links work correctly. Make sure forms collect data properly. Review site security settings. Check for any broken images. Ensure your website is mobile-friendly. Confirm site speed is fast. Test site navigation for ease of use. Validate your site’s HTML and CSS code. Double-check your SEO settings.
Publishing Your Theme
First, make sure your theme is ready. Test it well. Check every detail. Next, log into your WordPress dashboard. Find the “Appearance” tab. Click on “Themes”. Look for the “Add New” button. Select it. Then, choose the “Upload Theme” option. Browse your computer. Find your theme file. It should be a .zip file. Upload it. Wait for the upload to finish. Once done, activate your theme. Your theme is now live. You can see it on your site.
Prepare your theme for sharing. Follow WordPress guidelines. Go to the theme directory page. Create an account if needed. Log in. Click on “Submit a Theme”. Fill in the form. Enter all required details. Upload your theme file. Submit it. Wait for review. The team will check your theme. If it meets standards, it will be listed. Many users can then see and use your theme. It’s a great way to share your work.
Frequently Asked Questions
How To Build Custom Themes In WordPress?
To build custom themes in WordPress, start by installing WordPress locally. Create a new theme folder in “wp-content/themes” and add essential files like style. css, index. php, and functions. php. Use HTML, CSS, and PHP to design your theme. Test thoroughly and upload to your WordPress site.
How Do I Create A Custom Style In WordPress?
Create a custom style in WordPress by editing the theme’s CSS file. Access Appearance, then Customize. Add custom CSS code. Save changes. Use a child theme to prevent overwriting during updates. Consider plugins like Simple Custom CSS for easier management.
Always back up your site before making changes.
Which Theme Builder Is Best For WordPress?
Elementor is a top choice for WordPress theme building. It offers user-friendly drag-and-drop features. Divi is another excellent option with a robust visual editor. Both provide extensive customization capabilities, making them popular among developers and designers. Choose based on your specific needs and preferences for the best experience.
How To Create A Custom Theme In WordPress Without A Plugin?
To create a custom WordPress theme, set up a local environment. Create a new theme folder in wp-content/themes. Develop essential files: style. css, index. php, and functions. php. Use HTML, CSS, and PHP for design and functionality. Test and activate your theme through the WordPress dashboard.
Conclusion
Creating a custom WordPress theme enhances your website’s uniqueness. Follow the steps carefully for a smooth process. Start with basic HTML and CSS. Add PHP for dynamic content. Test your theme on different devices. Fix any errors promptly. Keep learning new techniques.
Your efforts will pay off with a personalized site. Always update your skills. Explore online resources and tutorials. Enjoy the creative journey. With dedication, your custom theme will shine. Your website will reflect your personal style. Happy designing!