Have you ever wondered how to host a web server on Linux? You’re not alone.
Many people dream of running their own website, but the technical jargon can be overwhelming. You might think it requires a degree in computer science, but the truth is, it’s much simpler than you imagine. By the end of this article, you’ll see just how easy it can be.
Imagine the satisfaction of knowing you have complete control over your own server. You can tailor it exactly to your needs, enhancing both your skills and your website’s performance. Ready to demystify the process and take the first step towards becoming a web hosting pro? Keep reading to unlock the secrets of hosting a web server on Linux.
Credit: www.youtube.com
Choosing The Right Linux Distribution
Ubuntu is a favorite choice. Easy to use and beginner-friendly. It has a big community. Lots of help available.
CentOS is another option. Known for stability. Many big companies use it. Strong security features.
Debian is reliable. It’s very stable. Many servers trust it. Great for experienced users.
- Ease of use is important. Choose a simple system.
- Community support helps. Bigger communities offer more help.
- Security matters. Ensure strong protection features.
- Compatibility with software. Check software support.

Credit: www.veeble.com
Installing Linux
First, check your computer specs. Ensure it meets Linux system requirements. Your computer should have at least 2 GB RAM and 20 GB free space. Make sure you have a USB drive for installation. Download a Linux ISO file from a trusted site.
Plug the USB drive into your computer. Restart the computer and enter boot menu. Select the USB drive to boot from. Follow the on-screen instructions to install Linux. Choose partition options carefully. Set up a username and password for security. Let the installation finish. Once done, restart your computer. Your new Linux system is ready.
Configuring Network Settings
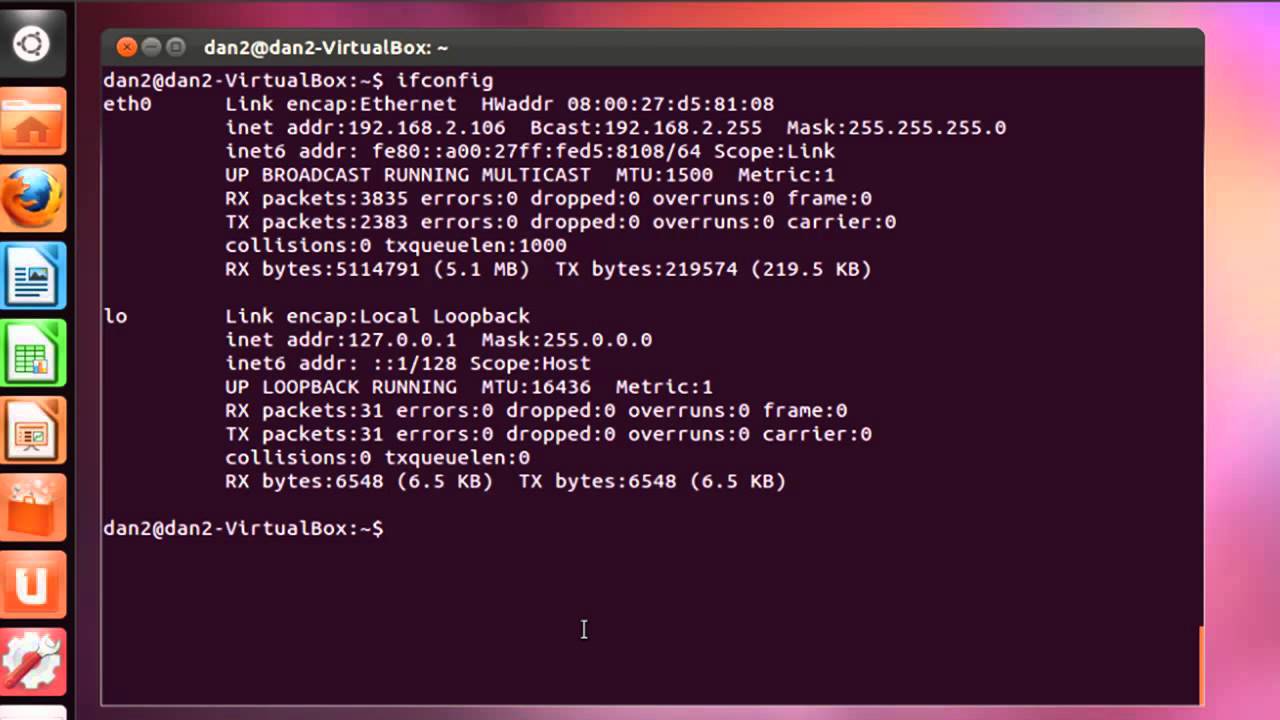
Assigning an IP address is key. Use the ifconfig or ip command. Check your current IP with these tools. To assign a new IP, type the command: sudo ifconfig eth0 192.168.1.10. Replace 192.168.1.10 with your chosen IP. This IP should be within your network range. Save your settings to make them permanent. Edit the /etc/network/interfaces file. Add your IP details here. Save and exit the file. Restart your network to apply changes.
DNS settings are crucial for web servers. Edit the /etc/resolv.conf file. Add your DNS server details here. Use Google’s DNS as an example. Type nameserver 8.8.8.8 in the file. Save your changes. This helps translate domain names to IPs. Test your DNS settings using the nslookup command. Ensure your server can resolve domain names. If issues arise, check your entries. Verify the DNS server IPs. Correct any typos or errors.

Credit: www.ubuntumint.com
Setting Up Apache Web Server
Apache is a popular web server software. It is free and open-source. To install, open your terminal. Type sudo apt-get install apache2. Press enter and wait. The system will ask for your password. Type it and press enter. Apache will begin installing. It might take a few minutes. Once done, Apache is ready.
You can make Apache fit your needs. First, open the Apache config file. Type sudo nano /etc/apache2/apache2.conf. This opens the configuration file. You can change settings here. Want a different port? Change the number in the file. Want more security? Look for security settings. After changes, save the file. Type sudo service apache2 restart. This restarts Apache with new settings.
Securing Your Web Server
Hosting a web server on Linux involves ensuring robust security measures. Protect your server by updating software regularly and using firewalls. Implement strong passwords and monitor for unauthorized access to maintain a secure environment.
Firewall Setup
A firewall protects your web server. It blocks unwanted traffic. Set rules to allow only necessary connections. Use software like UFW or iptables. They are easy to set up. Allow traffic only from trusted sources. This keeps your server safe.
Regularly update your firewall rules. This ensures protection against new threats. Monitor logs for any suspicious activity. Logs help in identifying issues early. Make sure your firewall runs all the time.
Implementing Ssl Certificates
SSL Certificates encrypt data between users and your server. This ensures data privacy. Install certificates from trusted providers. Let’s Encrypt offers free certificates. They are easy to use. Secure every page of your website.
Renew your SSL certificates regularly. This avoids expired certificates. An expired certificate may cause security issues. Keep your server software updated. Updates fix security holes. They enhance SSL performance.
Managing Files And Directories
Setting up a web server on Linux involves organizing files and directories effectively. Proper management ensures smooth operation and easy navigation. Simple steps can help keep everything accessible and secure.
Organizing Web Files
Keeping your web files neat is key. Create folders for images, styles, and scripts. This makes it easier to find things. Use clear names for folders and files. This helps everyone understand where things are. It also makes the server work better. Keep your website files in one main folder. This main folder is often called the “root” folder. Inside this, make separate folders for different types of files. This keeps everything sorted.
Permissions And Ownership
Permissions control who can see or change files. Ownership tells who the file belongs to. Every file has an owner. You can set permissions to allow reading, writing, or both. It’s like giving keys to a house. Use commands like `chmod` to change permissions. Use `chown` to change ownership. Be careful with these settings. Wrong settings can let anyone change your files.
Monitoring And Maintenance
Ensuring a Linux web server runs smoothly involves regular monitoring and maintenance. Check server performance and update software. Address issues promptly to prevent downtime and security threats.
Tracking Server Performance
Regular monitoring keeps your server healthy. Check CPU usage often. Low CPU usage means faster server. Watch out for high memory use. High memory slows down the server. Look at disk space too. No space means trouble. Use tools like Nagios or Zabbix. These tools help track performance. They alert you when something’s wrong. Keep logs for future checks. Logs show past server issues. This helps fix problems faster.
Regular Updates And Backups
Updates are very important. They keep the server secure. Install updates monthly. Backup your server data often. Backups save important files. Use tools like rsync or tar for backups. These tools are easy to use. Store backups in safe places. Use cloud storage for backups. Cloud storage is reliable. It protects data from loss. Never skip backups. Backups save you from data loss.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Identifying server errors can be tricky. Check error logs first. Logs show what went wrong. Look for red flags. Common errors include “404” or “500”. “404” means page not found. “500” means server problem. Fixing these needs attention. Check file paths for “404”. Check server settings for “500”.
Solutions for Common Problems can help. Restart the server first. Sometimes, a simple restart fixes issues. Update software regularly. Updates can patch bugs. Secure your server well. Use strong passwords. Limit access to important files. Monitor server activity. Regular checks prevent issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Linux Os Is Best For Web Servers?
Ubuntu Server is ideal for web servers due to its reliability and extensive community support. CentOS offers stability and long-term support, making it a popular choice. Debian provides strong security features and flexibility, perfect for advanced users. Choose based on specific requirements and expertise level.
How To Create An Http Server In Linux?
Install Apache using the command: `sudo apt-get install apache2`. Start the server with `sudo systemctl start apache2`. Verify by accessing `http://localhost` in a browser.
How To Create A Virtual Server In Linux?
Install a hypervisor like VirtualBox or KVM on your Linux system. Create a new virtual machine. Allocate resources such as CPU, RAM, and disk space. Select an ISO file for the Linux distribution. Start the virtual machine and follow the installation instructions.
Your virtual server is now ready.
How To Make A Webpage On Linux?
Install a text editor like Vim or Nano. Write your HTML code. Save the file with a. html extension. Open the terminal. Use a web server like Apache or Nginx to host the file. Access your webpage through a browser by entering the server’s IP address followed by the file name.
Conclusion
Setting up a Linux web server is simpler than it seems. With the right tools, anyone can do it. Start by selecting a Linux distribution that fits your needs. Next, install necessary server software like Apache or Nginx. Configure security settings to protect your server.
Regular updates ensure smooth operation. Always monitor server performance for any issues. Troubleshooting keeps your server running efficiently. Practice makes perfect, so keep learning and experimenting. Hosting a Linux web server empowers your online presence. Dive in, explore, and enhance your skills.
With patience, you’ll become more confident and capable.